
 Home
KS4
A2
Opts
Gall
Dates
KS3
Home
KS4
A2
Opts
Gall
Dates
KS3



 Tuts
Tuts







 Research
Specification
Designing
Evaluation
Task Analysis
Research
Specification
Designing
Evaluation
Task Analysis

 Making
Making

|
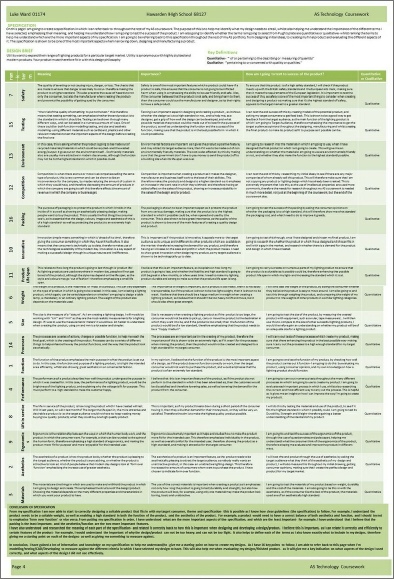
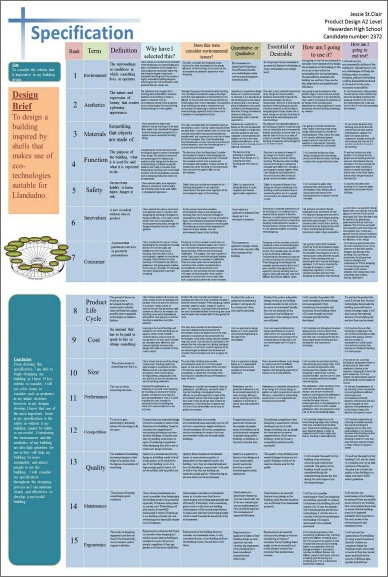
Specification |
Definition & Research Findings |
Qualitative or Quantitative? |
Essential or Desirable? |
Importance |
How am I going to test the success of the product? |
|
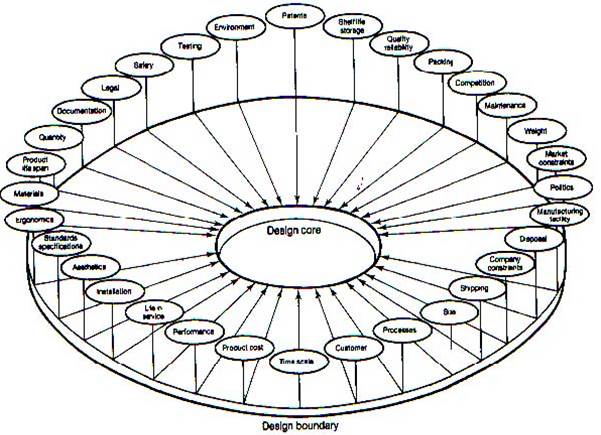
Aesthetics |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Consumer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Environment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Safety |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Size |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Materials |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Life Cycle |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Packaging |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ergonomics |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Anthropometrics |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Timescale |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Performance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Innovation |
|
|
|
|
|




|
AS Developing a Specification |
Marks |
|
A detailed and relevant specification developed from the product analysis The specification displays a hierarchy of criteria, some of which are measurable and take account of the relative importance of a wide range of factors.
|
9- |
|
Analyse research and developing a design specification |
Marks |
|
Detailed analysis of the design situation has led to appropriate and well- Research using ICT where appropriate has been carefully analysed, as a result of which the candidate has demonstrated a thorough understanding of the task and the requirements which have to be met. Evidence of students' ability to reflect upon their research and analysis and make objective comment on the way forward. A detailed and relevant specification which displays a hierarchy of measurable criteria which takes account of the relative importance of a wide range of factors which will drive designing.
|
9- |







































| KS3 Research |
| GCSE Research |
| A2 Research |
| KS3 Specification |
| GCSE Specification |
| A2 Specification |
| KS3 Designing |
| GCSE Designing |
| A2 Designing |
| KS3 Evaluation |
| GCSE Evaluation |
| A2 Evaluation |
| KS3 Task Analysis |
| GCSE Task Analysis |
| A2 Task Analysis |
| KS3 Manufacturing Spec |
| KS3 Materials |
| GCSE Manufacturing |
| A2 Manufacturing |