Home
KS4
A2
Opts
Gall
Dates
KS3
Home
KS4
A2
Opts
Gall
Dates
KS3



Copyright © 2012 M.Kenny. All Rights Reserved
No parts of this website maybe copied or reproduced without permission
 Tuts
Tuts







 Research
Specification
Designing
Evaluation
Task Analysis
Research
Specification
Designing
Evaluation
Task Analysis

 Making
Objs
Ass
Ext
Making
Objs
Ass
Ext
A design brief is a written explanation - given to a designer - outlining the aims,
objectives and milestones of a design project.
A thorough and articulate design brief is a critical part of the design process.
It helps develop trust and understanding between the client and designer - and serves
as an essential point of reference for both parties.
Above all, the design brief ensures that important design issues are considered and
questioned before the designer starts work. It may contain some functional requirements,
aesthetics, materials, safety and quality considerations and other design constraints.
The brief will guide the designers and help them formulate a performance and marketing
specification.
The client is usually the person who has identified the need and provides the brief.
It is the responsibility of the designer to work closely with the client to ensure
that they get the product they want. It is also crucial designers make use of market
research and fully understands the needs and wants of the ‘user’ or ‘customer base’
they are designing for.
In industry designers maybe part of a team, as they are unlikely to have expertise
in all areas. In the design of a personal music player such as the IPod, designers
would be split into teams working on styling, electronics, software and control systems,
ergonomics and interface. These teams may have particular expertise in those areas
but may use external consultants.
Another example is in the car industry: the design of a vehicle would be shared among
many designers who would be specialists in specific areas, including mechanical engineering
(for engine and mechanical systems), software engineering (for engine management
and instrumentation), textiles (for seating, carpets, etc.), and so on. Designers
of cars would work with production engineers to plan the manufacture but specialist
industrial designers would design the machines that make the cars.

Although not mandatory it is suggested that candidates should begin to use A2 size
paper for the coursework, as a preparation for the AL project. That being the case
the following guide should give a clear indication of the amount of design work which
is expected, from the majority of candidates.
(i) Research and analysis - 4 sheets
(ii) Design Brief and specification - 1 sheet
(iii) Design considerations and investigation - 3 sheets
(iv) Generating proposals - 4 sheets
(v) Development details - 2 sheets
(vi) Detail designing - 2 sheets
(vii) Planning/Quality Assurance/Quality Control - 1 sheet
(viii) Evaluation - 2 sheets
These figures are given as an approximate guide only – examiners will assess the
design and make task against the published assessment criteria rather than by the
number of design sheets or report pages. It is suggested that, as an alternative
to including material in the A2 sized design folio, the planning, section and use
of materials, evaluation and economic factors (costings) content could form the basis
of an A4 project report as described at the end of this resource.

Design and technology should be the subject where mathematical brainboxes and science
whizzkids turn their bright ideas into useful products
James Dyson


Task Analysis Introduction
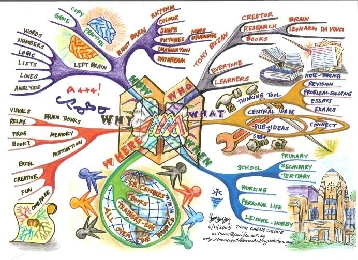
A mind map is a good method to help you analyse the problem in more detail and gives
you lots of useful avenues to explore. Remember to be adventurous at this stage,
do not forget to write down all thoughts no matter how silly, weird or wacky! These
often lead to the most unusual solutions or the best designs and show risk taking
which leads to higher grades. We use something called ACCESS FM throughout the design
process to help guide our thinking and provide a starting point. You can add your
own categories if you think this will help. ACCESS FM stands for aesthetics, consumer,
cost, environment, size, safety, function and materials. This model can be used throughout
your folder to analyse your research, produce a specification and evaluate your ideas
and product.
Tut
Context & Design Task
There is no single "right" way to produce a task analysis page. The pages and examples
shown are for guidance only and students are encouraged to layout their pages as
you see fit. Hover over the sections of the page for hints and tips…………………………….
In order to help you fully analyse the task follow the steps below
- First task is to copy down the context from your chosen task.
- List or highlight the key words found within the context.
- Copy down your chosen design brief.
- List or highlight the key words found within the design brief.
- Collect initial images of anything and everything to do with your brief to help inspire
you.
Tut





























Pro Design Words
Pro-design words can be used to aid your task analysis and provide you with lots of avenues to explore. You can identify if form is more important than function or vice versa. Click on the presentation icon above and look over the inspiration for a design brief presentation adding onto your task analysis mind-map as you go along. Below are some examples of pro- design words. Research them further and list the most important pro-design words you think will influence your designing.
 Ext
Ext



















Key Factors that influence the design of a product.
The chief enemy of creativity is 'good' sense.
Pablo Picasso










Can you think of anything of any other key factors? List them on your task analysis
page
What are the key factors that will effect the design of your product?
Key aspects to take into account when designing: it is important when designing products
to take several key factors into consideration in order to be successful. The order
of these considerations varies according to the design brief or the individual.
Ext
Clever Product Design inspiration
Ext
Ext
Ext





























Task Analysis Mind-map
There is no single "right" way to produce a task analysis mind-map. The pages and
examples shown are for guidance only and students are encouraged to layout their
pages as you see fit. Below only gives you some key aspects that you can explore
add more of your own using ACCESS FM to help.
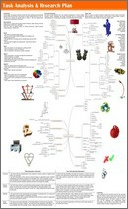





















Aesthetics
- What do you intend your product to look like?
- What colours, styling, patterns do you intend to design your use?
- How important are aesthetics?
- Is form more important than function?
- What theme or inspiration will you use?
- Will you carry out market research, research an art movement, a theme, make observations
and drawings to inspire you. Collect images?

Consumer
- Who do you intend your consumer to be?
- Who are you are designing for at this stage or will you determine this as you research
or design your product?
- How old they are?
- What is their profession?
- What interests they have?
- How much money they earn?
- How will you collect information about your target market

Function
- Is form more important than function or vise versa?
- Will your product be multifunctional? If so why?
- What information will you need to research in order to manufacture your product?
Make your product work?
- Will you need to know about light fittings, electrical components, springs, mechanisms
etc?


Materials
- You may not know exactly what materials you will be using yet however you should
have an idea of the sort of product you will make i.e. Cheap, low quality, high quality,
expensive. This will have an effect on what type of materials you will use:
- high quality materials such as...
- cheap materials such as...
- You may also you the sorts of properties different materials have such as thermal
etc.
Task Analysis Extension Categories
Can you add any more categories to extend your mind-map even further. Hover over
the examples below.
- Cost
- Environment
- Safety
- Size
- Lifecycle
- Packaging
- Ergonomics
- Anthropometrics
- Timescale
- Performance
- Innovation
 Start
Start




|
Product Analysis and Research
|
Marks
|
|
Detailed product analysis has led to appropriate and well-focused research.
The intended product has been carefully analysed for, 'above' and 'below the line'
criteria.
The candidate has demonstrated a thorough understanding of the task ahead and the
requirements which have to be met to satisfy the needs of the target audience.
|
18-20 Marks
|
|
Analyse research and developing a design specification
|
Marks
|
|
Detailed analysis of the design situation has led to appropriate and well-focused
research.
Research using ICT where appropriate has been carefully analysed, as a result of
which the candidate has demonstrated a thorough understanding of the task and the
requirements which have to be met.
Evidence of students' ability to reflect upon their research and analysis and make
objective comment on the way forward.
A detailed and relevant specification which displays a hierarchy of measurable criteria
which takes account of the relative importance of a wide range of factors which will
drive designing.
|
9-10 Marks
|





Who, Why, What, Where and When
Who will be the intended target user?
Who can I ask to suggest any improvements that can be made to the product?
Who can I ask for help if I need any during the designing, testing and manufacturing
stages?
Who are the competitors for the product that I am going to manufacture?
Who will influence the design and manufacture of the product?
Why is the product I am designing and making a solution to the task?
Why are the materials that I am going to use to manufacture the product suitable?
Why is it important to recycle?
Why is sustainability an important issue in today's world?
Why will I need to carry out research and carry out testing on materials?
What is the product that I am going to design and manufacture for a specific target
user group?
What will I need to research in order to design and manufacture the product?
What equipment will I need to manufacture the product?
What properties of what materials will I need to test?
What can I recycle to make the product?
When will the project need to be completed by?
When should I start designing the product in order to finish the project within the
deadline set?
When should I start to test materials?
When should I make a prototype of the product that I am going to manufacture?
When should I start manufacturing the final product?
Where will I gather relevant research from?
Where will the product be manufactured?
Where can I test possible materials that I could use to manufacture the product?
Where will the product be promoted and marketed?
Where will I obtain the materials that I need in order to manufacture the product?
Conclusion - Checklist
What are the next steps? Do you need to narrow don your research to make it more
focused? Do you need to produce a research plan to help formulate your thoughts and
give you clear direction?
Identifying a need
Explain the following to define the design situation clearly in words and drawings/photographs:
what are the aims of the project;
who is the product intended for, the target audience;
how often is the product likely to be used;
where will the product be used;
will the existing environment affect the design of the product?
Identify user needs
list all the qualities that you think the intended user may demand of your product;
undertake market research on your target audience to establish their wants/needs;
present a comparative analysis of your results.
Design considerations
explain the design features that you think your product must have;
assess the importance of a range of design considerations to your design task;
describe any unique selling points or special features that your product might
have.
Research
identify relevant knowledge and understanding that you will need to help you when
designing;
identify the likely sources of this information;
include a section in your folio that contains the information that you intend using;















Step 1 - Introduction:
This is a statement that should:
- describe what activities you are going to carry out and explains why in terms of
progressing your coursework.
Say how this will be helpful in your project
Step 2 - The Task:
- Here you should include a copy of the design task you have chosen or developed yourself.
- You may wish to underline parts of the task that will require analysis in a mind
map.
Step 4 - Key words:
- List the key words from your design task that you can analyse in your mind-map.
- List the key words used in your initial research images that you can analyse in your
mind-map.
Step 5 - Pro-design words:
- Collect some initial images related to your design Pro-design words can be used to
aid your task analysis and provide you with lots of avenues to explore. You can identify
if form is more important than function or vice versa.
- Using the presentation below research them further and list the words you think you
will influence your designing, list them and further analyse them in your mind-map.
Step 6 - Personal Statement:
- Write a paragraph about yourself. Try to discuss your interests in terms of Design
and Technology as opposed to how many brothers and sisters you have.
- Discuss your future plans
- Discuss examples of existing design work that you have produced in the past.
Step 7 - Design Philosophy:
- Discuss who your favourite fashion designer/product designer/architect/chef is.
- Discuss examples of existing design work that you think is good.
- Discuss what inspires you when designing and what your priorities are. Is sustainability
a priority or is aesthetics more important than functionality?
Step 3 - Initial Research:
- Collect some initial images related to your design task.
- Analyse images that interest you in your mind-map. For example the characteristics
in art deco (zigzags, symmetrical, sunrises).








What materials could you use in the packaging of the product? Are they suitable,
could they be used to mass produce your product? Will the materials be environmentally
friendly? Will they be able to be recycled or reused at the end of the products life?
What symbols and warnings would you include on the packaging? How could you cut down
the packaging environmental footprint? Will your product be flat packed? Will this
effect the size and transportation costs of your product?
What materials would you use in the manufacture of the product? Are they suitable,
could they be used to mass produce your product? Will they be easy to mark out, cut,
shape and finish? How will you finish the product? Will the materials need to be
environmentally friendly? Will they be recycled or reused at the end of the products
life? Could you improve upon your material selection? Does your material selection
impact upon the products lifecycle?
What ergonomic considerations will you need to take into account? Are there going
to be any components that will need changing such as bulbs or batteries? Will access
need to be easy to get to? Does it need colour coded interfaces to explain how to
use or interact with the product? Will the product move or need to be moved? What
ergonomic considerations will need to be taken into account if this is the case?
Do you need to consider SPURC (strength, posture, user group, reach or clearance)?
What anthropometic considerations do you need to take into account? Use SPURC (strength,
posture, user group, reach or clearance) to identify the key criteria that you will
need to consider to design a successful product.
What percentile do you need to take into consideration? 5th, 50th or 95th percentile
range?
- Anthropometrics is the study of body measurements and statistical data concerning
the sizes and shapes of the population.
- Ergonomics is the relationship between a product and its users.
- All people fall into the 5th, 50th and 95th anthropometric percentile range.
- User group, posture, clearance, reach and strength are all important factors in anthropometrics
and ergonomics.
What timescale are you working with? Are there any special considerations that you
must take into account:
- Material delivery time
- Testing and prototyping
- Time to laser cut, 3D print, manufacture?
- Gluing time?
- Finishing time (i.e. Sanding, sealing etc)?
- Finish drying time?
Can you estimate time scales for the main activities you think you will need to undertake?
Do you have opportunities to build in contingencies?
What innovative features can you include in the design of your product? What can
you include to give your design the edge? What is your interpretation of innovation.
Look at your pro-design words such as modular, multi-functional, foldable, flat packed
etc.
What price range will your product fall into? Will it be expensive, cheap, mid range,
if so why? What materials, processes and finishes will you use, does this reflect
the cost? Will the cost reflect the quality of the product? Will the cost of your
product a result of what manufacturing processes (mass produced, batched produced,
one off) you will use to commercially produce it? What will your potential consumer
expect to get for their money?
How will the product effect the environment: When it will be made (manufacturing
process): materials used, energy used? When its being used, will it give off any
emissions or pollution? When it is disposed of, will it be recyclable, will it be
able to be reused? How will you reduce the products carbon footprint?
How safe will the product be to use? What are the dangers of using your product (sharp
edges, toxic paints, electric components, weight etc.) How will you make it safe
for the intended user (example;. “all electrical components will be housed in a waterproof
casing or raised”)? How will you reduce the risk of injury?
How big will the product generally going to be? How big will certain parts of your
product be? Will you make it adjustable? How big do you potential consumers expect
the product to be? Are there any critical sizes you must take into consideration?
If space is limited how will you maximise this?

 Home
KS4
A2
Opts
Gall
Dates
KS3
Home
KS4
A2
Opts
Gall
Dates
KS3



 Tuts
Tuts







 Research
Specification
Designing
Evaluation
Task Analysis
Research
Specification
Designing
Evaluation
Task Analysis

 Making
Objs
Ass
Ext
Making
Objs
Ass
Ext